Different design paradigms. In 1969, they had one shot to get everything right, and prepared accordingly (not to mention, they had a massive budget since the space race was all part of the cold war).
SpaceX is taking a different approach, fail fast and cheap. They are taking an iterative approach that allows them to learn from previous failures, rather than anticipating what all those failures could be and then over engineering the rocket to prevent that.
They are different approaches, and each has their own pros and cons. ¯\_(ツ)_/¯
That’s a great summary, I appreciate it. Do you think the new approach has been worth it so far? The Artemis 1 launch was successful first try.
The Artemis 1 launch was also staggeringly expensive, and yet to be repeated.
In the time it’s taken to develop that rocket, SpaceX has gone from it’s very first real flight (by which I mean actually achieving something, rather than a pure test flight) to launching far more every year than the entire rest of the world combined. Note that by that definition, Artemis hasn’t had a single “real” flight yet.
SLS did a lap around the moon flawlessly and returned safely.
Starship, a scale model of the empty shell that HLS might one day sit in, when it is finally developed, can’t even land without exploding.
According to a recent speech by musk, it wasn’t even the real shell. IFT3 was a 40ton-to-LEO craft, where HLS will have to be around 100, which would take the as of yet unflown and (mostly?) unbuilt “Starship 2”.
And where SLS will simply have to do a repeat of what it has already done for Artemis 2.
HLS will have first be actually built, get launched, get refueled by a tanker craft that also doesn’t exist yet, an unknown number of times (probably 12), fly to the moon, land there, take off, come back, land on earth and then do ALL of that again in time for Artemis 3 where it will have people on board.
SLS is 1 for 1, and if Starship IFT4 does everything right tomorrow, HLS is still at 0. And if it does everything right, I will buy a hat and eat it.
They have completely different goals. If SpaceX wanted to throw out the Starship and Booster sections every time, they’re already as capable as the Artemis launcher. But they are looking longer term, and want to also be 1000x cheaper.
It took them dozens of launches to be able to re-use a Falcon9. They’ll get there eventually.
Nobody thought they’d get Falcon 9 to launch, and they did. Nobody thought they’d get Falcon 9 to land, and they did. Nobody thought they’d be able to re-use a Falcon 9 enough to make it worth the investment, and they did.
Doesn’t mean they’ll succeed, but it does mean they have a good track record.
Easy answer. Far less money is being given today to NASA:
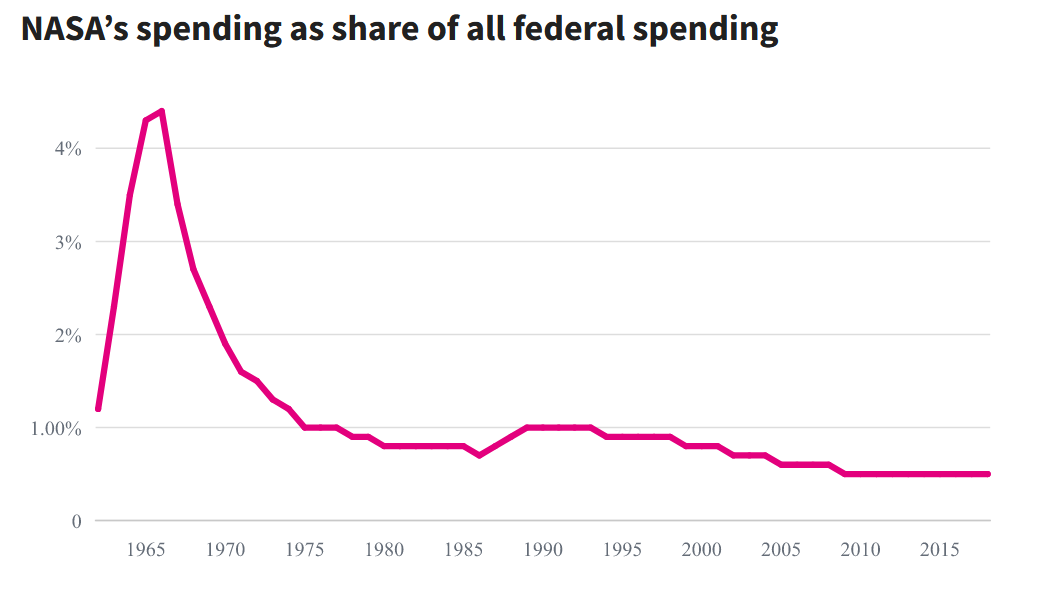
Further, that NASA budget includes all the extra planetary science happening (multiple Mars rovers, Deep Space network, LEO space station operations, deep space probes like DART, Juno, OSIRIS-REx, etc, plus all of the atmospheric flight stuff like the low noise supersonic flight experiments. This also includes all of SLS which is a SECOND rocket being made for Moon exploration.
To answer your second question: yes, reuse is worth it. We didn’t do it during Apollo because it would have been even more expensive. Because we didn’t have it, any flight was just as expensive as the first. So we had to stop going unless the crazy amount of money would stay, which it wouldn’t.
Several reasons.
1 - SpaceX is a startup company. They run on venture capital, and unlike NASA who gets a big bag of taxpayer money, SpaceX has to promise new investors something better every year. And since SpaceX hasn’t come close to turning a profit, they need to do it by making spectacle. Launching Rockets is spectacle. Traditional companies can take their time to get it right, but SpaceX can’t draw in the venture capital they need to survive based on one succesful launch every other year. But they can get money with slightly less shitty failures.
2 - SpaceX is using an entirely new type of engines, burning liquid methane instead of kerosine or hydrogen, and making rocket engines is… well… rocket science. The problem is mostly that it’s really really hard to get engines to relight when you don’t have gravity, and especially hard when it’s methane you’re burning. This is why Apollo used hypergolic engines (fuel that will burn when it touches, instead of needing to be lit) for everyone but the main launch.
3 - SpaceX only got the contract for the lunar lander because the head of the lunar lander program, Kathy Lueders, gave them (and not the other parties) a private call to tell them the exact budget available. Then she awarded the contract to SpaceX, for being the only party to submit a bid within the budget. (Source: https://ecf.cofc.uscourts.gov/cgi-bin/show_public_doc?2021cv1695-77-0 the court opinion where they spell out this was legal, and say nothing on wisdom or ethics, pdf alert). Incidentally she now has a cushy and well-paid job at SpaceX.
4 - NASA recently paid a second party, blue Origin, to also develop a lunar lander, so feel free to take that as you will. It’s probably not a sign of trust in SpaceX… so I’m willing to say that point 5 is that either SpaceX is shit at this (unlikely, since Falcon 9 is pretty awesome) or they’re just not taking it seriously.
Point 1: SpaceX’s entire development philosophy is “test early, test often and learn from failures”. This is a much quicker pace than simulating every imaginable failure scenario and leads to faster progress in development. With the Falcon 9, that process proved wildly efficient and successful, culminating in a launch vehicle so reliable that it’s cheaper to insure a payload on an F9 that already has multiple launches under its belt than a brand new booster. And they’re turning enough of a profit to develop the Starship largely on internal funds, seeing how the early Raptor flight tests were before the HLS contract.
Point 2: Just adding, the Raptor engine is the first full-flow staged combustion engine to ever get off a testing stand and actually fly. The engineering complexity of these things is on the level of the Shuttle’s RS-25.
Point 3: SpaceX were the only ones with more than designs and mockups to present, and they had a reliable track history from working with NASA on the commercial resupply and crew projects. And I see no problem with awarding a contract to a bid that actually fits into the budget.
Point 4: Multiple options was always part of the plan. NASA wants redundancy, so that if one of the providers runs into problems, the other provider can continue (and perhaps even take up the slack) instead of everything coming to a grinding halt. For a perfect example, look at the Shuttle and Commercial Crew programs. The Shuttle got grounded and since it was NASA’s only manned launcher, they had to bum rides from the russians. In contrast, the CC contract was awarded to Boeing and SpaceX. With Starliner’s continued issues, SpaceX has picked up the slack and fulfilled more than their initial contract in launches, instead of NASA having to bum rides from the russians again. The initial HLS contract was supposed to go to two providers, until the budget got cut. Blue’s bid was always the favorite for the second pick.
SpaceX’s entire development philosophy is “test early, test often and learn from failures”. This is a much quicker pace than simulating every imaginable failure scenario and leads to faster progress in development.
This is a catchy statement, not an actionable philosophy. There’s many ways to do it, and it’s entirely possible that SpaceX is doing it poorly.
There’s a lot of value in brainstorming every imaginable failure scenario. It’s industry standard to do so in fact with HAZOPs. There’s failures that you may not necessarily see in testing – especially those that are rare but catastrophic. This is a field that should be acutely aware of that given past events.
There’s also a right way to do testing and a wrong way to do testing. You typically consolidate tests and do several at a time, depending on the stage in the project. And you don’t typically risk precious equipment in doing so.
From the sounds of it, they don’t have a robust safety program, and they’re hemorrhaging money and resources through poor testing philosophies.
To add on to what everyone else is saying, compared to the Apollo capsules, Starship is fucking HUGE. Apollo 11’s capsule was 10 feet tall by 13 feet in diameter. Starship is 180 feet tall not including the launch vehicle.
Also… Starship absolutely got into orbit, and could have completed the orbital insertion part of an Apollo style single use mission.
They just haven’t finished troubleshooting the re-use part yet. It’s already more powerful and cheaper than a Saturn V.
Other commentor answered very well. I’ll just add that if China or Russia starts sending successful ships to the moon/mars and/or starts making real steps for a moon base, then you can bet your ass the US government will pour all their resources into our space program. In other words, the Cold War boosted the space program in the 60s because Russia scary. During “peace-time”, the US government purposely under funds the living shit out of NASA. That’s why private corporations are doing it now, like SpaceX.
I agree, but I’m afraid these days they’d just farm it out to a private business instead of doing it themselves with the goal of doing it right like they did in the 60’s. Today they’d overpay some billionaire hugely for worse results because greed for profit = overcharging and substandard parts and oversight.
In the early 70s it was a risky and expensive one-time deal. Starship is doing it sustainably and will completely revolutionize space travel. I wouldn’t say they’re struggling they’re just still developing it.
The capabilities of starship are orders of magnitude more payload and for orders or magnitude less money at the same time.
Turns out it’s a bad idea to totally scrap a billion dollar rocket every time you use it.
Because politicians cared more about it back then, nowadays they’re too concerned about making the other political party “lose” than doing stuff to actually benefit the country’s citizens
Remember how Reagan and Thatcher told your parents that private corporations are (somehow) “more efficient” than state run organisations?
Yeah… they lied.
They are more efficient.
-
They are more efficient moving money from the bottom to the top and making investors and CEOs rich.
-
They are more efficient at making the minimum product for the price while suppressing labor, reducing customer service, and enshittifying the product as the lifespan of the company progresses in order to do #1.
Well… since you put it that way - I’ll just have to concede.
-
.
reagan